What is a Heatmap? Types, How It Works, Examples
Appinio Research · 14.12.2023 · 35min read

Are you curious about how to gain deep insights into user behavior, optimize your strategies, and make data-driven decisions that genuinely resonate with your audience? Heatmaps hold the key to unlocking the secrets of user interaction across various digital platforms.
In this guide, we'll delve into heatmaps, exploring their types, benefits, practical applications, and best practices. Whether you're looking to enhance your website's user experience, streamline product development, or supercharge your marketing campaigns, heatmaps are the invaluable tool you need to get there.
What is a Heatmap?
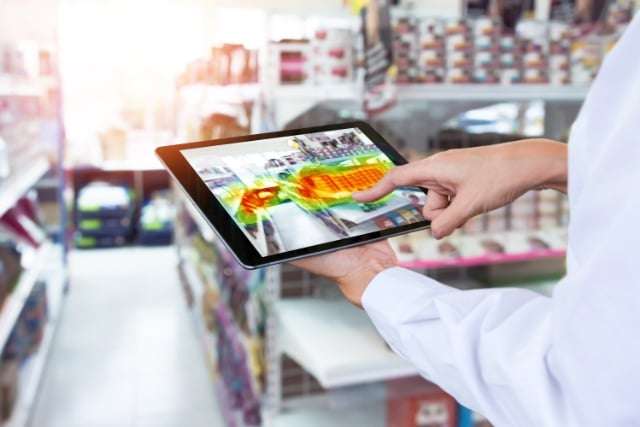
A heatmap, or heat map, is a powerful data visualization tool that provides a visual representation of data values in a matrix. It uses colors to represent the magnitude of a variable, making it easier to understand complex patterns and trends within the data.
Heatmaps are commonly used in various fields, including statistics, data analysis, and user experience (UX) design. They offer a simple and intuitive way to convey information, making them valuable tools for both experts and non-experts.
How Heatmaps Work
Heatmaps are created by mapping data values to a color scale, typically ranging from cool colors (e.g., blue or green) to warm colors (e.g., yellow or red). The color assigned to each data point corresponds to its value, with warmer colors indicating higher values and cooler colors representing lower values.
In the context of web analytics and user behavior, heatmaps are often used to visualize interactions on a website or app. They provide insights into where users click, scroll, move their cursors, or focus their attention. These interactions are then displayed as color-coded maps, allowing for easy identification of hotspots (areas of high activity) and cold spots (areas of low activity).
Importance of Heatmaps
Heatmaps offer many benefits that make them indispensable tools in various fields. Here are some key reasons why heatmaps are important:
- Visual Clarity: Heatmaps present complex data in a visually accessible format, making it easier to grasp patterns and trends at a glance.
- Data Exploration: They facilitate in-depth exploration of data, allowing users to uncover hidden insights and anomalies that may not be apparent in raw data tables.
- User-Centric Design: In UX design, heatmaps enable designers to understand how users interact with websites and apps, leading to user-centric design improvements.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Heatmaps provide actionable insights, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions for website optimization, product development, and marketing strategies.
- Efficient Problem-Solving: They help identify issues and areas of improvement quickly, whether it's optimizing conversion paths, fixing UI/UX problems, or refining content placement.
- Performance Evaluation: Heatmaps aid in evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, email engagement, and ad placements, guiding strategies for better results.
- Enhanced User Experience: By analyzing user interactions through heatmaps, websites and apps can be fine-tuned to offer a more engaging and user-friendly experience.
- Effective Communication: Heatmaps simplify the communication of complex data findings to stakeholders, making it easier to convey insights and recommendations.
Heatmaps play a vital role in transforming data into actionable insights, driving informed decision-making, and ultimately leading to improved user experiences, more effective strategies, and better outcomes in various domains.
Types of Heatmaps
Heatmaps come in various forms, each shedding light on a specific aspect of user behavior and interaction with your website. Let's explore the four main types of heatmaps in detail.
Click Heatmaps
Click heatmaps visually represent where users click most frequently on your web pages. They are a fantastic tool for understanding user engagement and identifying which elements are capturing their attention.
- What They Show: Click heatmaps use color gradients to highlight the intensity of clicks. Hotspots are areas where users click the most, while cooler areas receive less attention.
- Use Cases: Use click heatmaps to optimize the placement of buttons, links, and call-to-action elements. Identify which features or content users find most appealing.
Scroll Heatmaps
Scroll heatmaps track how far down a webpage users scroll, helping you gauge their interest in your content. Understanding scroll behavior is essential for ensuring your content is engaging and well-structured.
- What They Show: Scroll heatmaps typically use color coding to indicate scrolling patterns. They reveal whether users read your content fully, partially, or not at all.
- Use Cases: Use scroll heatmaps to determine where users lose interest and whether important content is getting enough visibility. This insight guides content placement and formatting.
Mouse Movement Heatmaps
Mouse movement heatmaps offer a glimpse into the path users' cursors take as they navigate your website. This data helps you understand areas of interest, hesitation, or confusion.
- What They Show: Mouse movement heatmaps display cursor movement patterns, highlighting where users hover, linger, or quickly move away.
- Use Cases: These heatmaps are invaluable for identifying points of interest within your content or design. They can reveal where users are unsure about taking action or where additional information might be needed.
Eye-Tracking Heatmaps
Eye-tracking heatmaps provide insights into where users focus their attention on a webpage. By visualizing gaze patterns, you can optimize the layout and placement of key content.
- What They Show: Eye-tracking heatmaps use heat zones to represent areas of a webpage that receive the most and least attention. Hotspots indicate where users' eyes linger the longest.
- Use Cases: Use eye-tracking heatmaps to improve the visual hierarchy of your web pages, ensuring that essential elements, such as headlines and calls to action, are in the users' line of sight.
Understanding these four types of heatmaps and how to interpret their data is essential for making informed decisions about website optimization and user experience enhancement.
Benefits of Using Heatmaps
Heatmaps offer a multitude of advantages that can significantly impact your website's performance and user experience.
- Visual User Behavior Insights: Heatmaps provide you with clear, visual data on how users interact with your website, making it easy to spot trends and patterns.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By analyzing heatmap data, you can make informed decisions about design, content placement, and optimization strategies.
- Enhanced User Experience (UX): Improving the user experience is at the core of heatmap usage. You can identify and rectify elements causing frustration, leading to a more enjoyable visit for your audience.
- Content Optimization: Heatmaps help you understand which parts of your content are resonating with users and which need improvement, ultimately leading to more engaging and compelling content.
- Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): By fine-tuning your website based on heatmap insights, you can increase conversion rates and achieve your desired goals, whether it's generating leads, making sales, or getting sign-ups.
- Problem Identification: Detect issues like dead-end pages, non-clickable elements, or confusing navigation early on, allowing you to address them promptly.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Heatmaps provide quick, actionable insights, reducing the need for time-consuming user surveys or extensive A/B testing.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly monitoring heatmaps allows you to make iterative improvements to your website, staying aligned with evolving user preferences and behavior.
- Competitive Edge: Utilizing heatmaps can give you a competitive advantage by ensuring your website offers a superior user experience compared to your rivals.
- Increased Engagement: Heatmaps can help boost user engagement by optimizing the placement of high-value content and interactive elements.
- Data-Backed Reporting: Heatmap data can be used to create data-backed reports and presentations to communicate findings and recommendations effectively within your organization.
- Strategic Design: Use heatmaps to strategically design your website by placing essential elements where users are most likely to engage with them.
These benefits highlight the immense value that heatmaps bring to your website optimization efforts and overall online success.
How to Create a Heatmap?
Creating and implementing heatmaps is a crucial step in gaining valuable insights into user behavior on your website. We'll walk you through the process, from selecting the right heatmap tool to configuring the settings for optimal results.
How to Select a Heatmap Tool?
Choosing the right heatmap tool is the foundation of your heatmap implementation. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed choice:
- Features: Look for heatmap tools that offer a comprehensive set of features, including click tracking, scroll tracking, and mouse movement analysis. The more features available, the deeper your insights can go.
- User-Friendliness: Opt for a user-friendly tool that offers an intuitive interface. This ensures that you can easily navigate and interpret the data.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the heatmap tool is compatible with your website's platform or content management system (CMS).
- Pricing: Consider your budget and choose a tool that offers a pricing structure that aligns with your financial resources.
While several heatmap tools are available, each with its unique strengths, Appinio stands out as a real-time market research platform that seamlessly integrates heatmap analysis into your decision-making process.
Experience the power of Appinio and elevate your data collection process. Ready to see it in action? Book a demo today!
How to Install Heatmap Tracking Code?
Once you've selected your heatmap tool, the next step is to install the heatmap tracking code on your website or product.
- Access Your Dashboard: Log in to your chosen heatmap tool's dashboard, where you'll find the tracking code snippet.
- Copy the Code: Copy the provided tracking code to your clipboard.
- Paste the Code: Access your website's HTML code, usually found in the header or footer section, and paste the tracking code there. Ensure it is placed just before the closing </head> tag.
- Save and Publish: Save the changes to your website's HTML code and publish your site. The heatmap tool will now begin collecting data.
Configuring Heatmap Settings
Configuring heatmap settings allows you to tailor the data collection process to your specific requirements. Here's what you need to consider:
- Frequency of Data Collection: Decide how often you want the heatmap tool to collect data. Daily, weekly, or monthly intervals are common choices.
- Pages to Track: Specify which pages of your website or screens of your app you want the heatmap tool to analyze. You can track specific pages, entire sections, or your entire website.
- Heatmap Types: Choose the types of heatmaps you want to generate, such as click, scroll, mouse movement, or eye-tracking. Selecting the suitable types depends on your goals and what you want to analyze.
- Segmentation: If your heatmap tool offers segmentation options, set up segments to analyze specific user groups or behaviors. This can provide more targeted insights.
- Event Tracking: Consider setting up event tracking to capture interactions with specific elements like forms, buttons, or videos.
By configuring these settings, you ensure that your heatmap tool collects the data most relevant to your optimization goals. Remember that heatmap data is only as valuable as the settings you define, so take the time to configure them thoughtfully.
How to Read a Heatmap?
Once you've implemented heatmaps and collected data, the next step is to interpret that data effectively. Let's delve into the specifics of each type of heatmap to help guide you through the process of understanding and deriving actionable insights.
Understanding Click Heatmaps
Click heatmaps are a fundamental tool for gaining insights into user interactions.
- Color Gradient: Click heatmaps use color gradients to represent click intensity. Hotspots, shown in warmer colors like red and orange, indicate where users click the most.
- Element Analysis: Identify which elements receive the most clicks. Focus on buttons, links, images, and other interactive elements.
- Click Path: Analyze the sequence of clicks. Are users following the desired path, or do they click randomly?
- Drop-off Points: Look for areas with no or minimal clicks. These may indicate ineffective or overlooked content or elements.
- Call-to-Action (CTA) Performance: Assess how well your CTAs are performing by examining their click-through rates.
Analyzing Scroll Heatmaps
Scroll heatmaps reveal user engagement with your content and how far they scroll down a webpage. Here's how to analyze scroll heatmap data:
- Color Coding: Scroll heatmaps use color coding to represent scrolling behavior. Darker colors indicate areas where users spend more time.
- Attention Zones: Identify "hot" zones where users tend to scroll to and spend time. These zones should ideally align with your key content.
- Fold Behavior: Pay attention to the "fold" line, which indicates the portion of the page visible without scrolling. Determine if essential content is visible above the fold.
- Drop-off Points: Observe where users stop scrolling. Sudden drop-offs can suggest a loss of interest or an issue with content layout.
Deciphering Mouse Movement Heatmaps
Mouse movement heatmaps reveal the paths users' cursors take as they navigate your website.
- Cursor Paths: Examine the paths users' cursors follow. Concentrated areas indicate points of interest, while erratic movements may signify confusion.
- Hover Behavior: Look for areas where cursors hover. Users often hover over elements they find exciting or clickable.
- Cursor Speed: Analyze cursor speed. Slow, deliberate movements may indicate engagement, while rapid movements suggest users are scanning.
- Behavior Changes: Notice changes in cursor behavior, such as abrupt shifts or hesitation. These can reveal user interactions or issues.
Using Eye-Tracking Heatmaps for Insights
Eye-tracking heatmaps provide valuable insights into where users focus their attention on a webpage. To extract insights from eye-tracking heatmap data:
- Heat Zones: Eye-tracking heatmaps use heat zones to indicate where users look the most. Hotspots represent areas of high visual interest.
- Focal Points: Identify the key focal points on your webpage. These are areas where users' eyes linger, such as headlines or images.
- Visual Hierarchy: Assess if the visual hierarchy aligns with your content goals. Ensure that essential information is within the users' line of sight.
- Attention Shifts: Observe any shifts in attention. Users may initially focus on one element and then move to another, which can help you optimize content flow.
Interpreting heatmap data requires careful observation and analysis. By understanding the nuances of each type of heatmap, you can pinpoint areas for improvement on your website and make data-driven decisions to enhance user experience and achieve your goals.
Common Heatmaps Use Cases
Heatmaps are versatile tools that find applications in various scenarios across websites, products, and more. Let's explore some everyday use cases to understand how heatmaps can be utilized effectively.
Website Optimization
Heatmaps are instrumental in optimizing websites of all kinds. Here's how they can be applied.
- Navigation Enhancement: Use click heatmaps to determine how users navigate your site. Identify which menu items, links, or buttons receive the most clicks, helping you streamline navigation.
- Content Engagement: Analyze scroll heatmaps to understand how users interact with your content. Optimize content placement and length based on where users drop off or engage the most.
- User Experience Improvement: By assessing mouse movement heatmaps, you can identify areas where users hesitate or encounter difficulties. This data informs design changes that enhance user experience.
- Conversion Rate Boost: Leverage click heatmaps to pinpoint areas for optimizing your conversion funnel, such as forms, checkout processes, and call-to-action buttons.
Product Development
Heatmaps offer valuable insights during product development, ensuring that your product meets user expectations:
- User Interface (UI) Design: Use click heatmaps to refine UI elements within your product. Identify which features users interact with most and which ones may require redesign.
- Feature Prioritization: Analyze click heatmaps to determine which features are popular and which are underutilized. This informs feature development and prioritization.
- User Onboarding: Track user interactions within your product using mouse movement heatmaps. Understand where users get stuck during onboarding and make adjustments to improve their experience.
- Bug Detection: Mouse movement heatmaps can reveal erratic cursor behavior, which may indicate user frustration or the presence of bugs. Investigate these areas for potential issues.
E-commerce Optimization
E-commerce platforms can benefit significantly from heatmap analysis, leading to increased sales and improved user satisfaction:
- Product Page Enhancement: Utilize click heatmaps to identify the most clicked product images, descriptions, and reviews. Optimize product page layouts accordingly.
- Shopping Cart Streamlining: Analyze scroll heatmaps to ensure a smooth transition from product selection to checkout. Identify drop-off points and streamline the process.
- Conversion Rate Maximization: By analyzing click heatmaps, you can optimize the placement and design of call-to-action buttons and trust signals to boost conversion rates.
- Checkout Page Optimization: Use scroll heatmaps to see if users abandon their shopping carts at specific points in the checkout process. Identify issues and reduce friction.
Marketing Campaigns
Heatmaps play a role in assessing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns:
- Email Marketing: Track clicks on email campaigns using click heatmaps. Understand which links and content elements generate the most interest among recipients.
- Banner and Ad Performance: Analyze click heatmaps for your website's banner ads and promotional elements. Optimize their placement and design based on user interactions.
- Landing Page Analysis: Evaluate user engagement with landing pages using click heatmaps. Adjust content and calls to action to align with campaign goals.
- A/B Testing: Combine heatmap analysis with A/B testing to validate the impact of marketing changes. Test variations and use heatmaps to identify winning strategies.
By considering these diverse use cases, you can harness the full potential of heatmaps to improve your website, products, and marketing efforts. Heatmaps empower you to make data-driven decisions that enhance user experiences, boost conversions, and achieve your business objectives effectively.
Examples of Heatmap Applications
Heatmaps are incredibly versatile tools, offering valuable insights across various scenarios. Let's explore more examples and scenarios where heatmaps can be applied effectively:
User Interface (UI) Refinement
When developing software or applications, heatmaps help fine-tune the user interface:
- Button Placement: Use click heatmaps to determine the optimal placement of buttons. Identify which button positions receive the most clicks, ensuring easy access to essential functions.
- Feature Usage Analysis: Analyze click heatmaps to understand which features users engage with the most. This insight informs feature prioritization and development efforts.
- Form Field Optimization: On web forms, mouse movement heatmaps reveal user behavior. Identify any form fields causing confusion or hesitation, leading to improved form design.
- Error Detection: Uncover issues within the user interface by examining mouse movement heatmaps. Erratic cursor movements can indicate areas where users encounter difficulties or confusion.
Mobile App Enhancement
Heatmaps are just as valuable for mobile app development:
- Screen Navigation: Use click heatmaps to track how users navigate through different screens and sections of your mobile app. Optimize the navigation menu and layout accordingly.
- In-App Engagement: Analyze click heatmaps to identify which in-app elements, such as buttons or tabs, users interact with most. Enhance the visibility of critical actions.
- User Onboarding: Similar to web applications, mouse movement heatmaps help improve the onboarding experience for mobile app users. Identify where users encounter obstacles and streamline the process.
- Gestures and Interactions: For touch-based apps, heatmaps can reveal how users interact with gestures. Determine whether users struggle with specific gestures or if they're underutilized.
Email Campaign Optimization
Heatmaps provide insights to enhance the effectiveness of email marketing campaigns:
- Link Engagement: Analyze click heatmaps to track which links within your email campaigns receive the most clicks. Optimize the placement of high-priority links and calls to action.
- Content Relevance: Examine click heatmaps to assess which email content sections garner the most attention. Use this data to tailor content to recipients' preferences.
- Design Impact: Heatmaps offer insights into how the email's design influences engagement. Adjust the layout and visual elements based on user interactions.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Ensure that email campaigns are mobile-responsive by examining how users interact with emails on various devices.
Case Study: Packaging Optimization for FMCG
In the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector, packaging plays a pivotal role in capturing consumer attention and driving purchasing decisions. Bonduelle, a renowned French company specializing in processed vegetables, faced the challenge of optimizing its packaging strategy to resonate with its target audience in Germany.
Bonduelle conducted a comprehensive packaging test, leveraging heatmap analysis to gain valuable insights into consumer preferences and behavior. By engaging 500 participants aged 20-65 across Germany, Bonduelle meticulously examined 19 key questions over a span of 5 hours in the field.
Key Objectives
- Identifying Purchase Decision Factors: Through heatmap analysis, Bonduelle aimed to pinpoint the decisive factors influencing consumers' purchase decisions when it comes to mixed salads and other packaged products.
- Gathering Target Audience Feedback: Heatmaps provided a nuanced understanding of how consumers interacted with different packaging designs, enabling Bonduelle to capture direct feedback from its target demographic.
- Crafting Optimal Package Design: By scrutinizing heatmap data, Bonduelle determined the most visually appealing packaging designs and identified essential elements to include for maximum consumer engagement and brand appeal.
Results and Impact
- Visual Appeal Insights: Heatmap analysis revealed insights into the visual elements that resonated most with consumers, guiding Bonduelle in crafting packaging designs that stood out on crowded shelves.
- Enhanced Consumer Engagement: By understanding user interactions through heatmaps, Bonduelle optimized packaging layouts to streamline navigation and highlight key product features, enhancing consumer engagement.
- Informed Decision-Making: Armed with heatmap data, Bonduelle made informed decisions regarding packaging design iterations, ensuring alignment with consumer preferences and market trends.
Incorporating heatmap analysis into its packaging optimization strategy, Bonduelle achieved significant improvements in consumer appeal and product visibility within the competitive FMCG landscape. This case study underscores the effectiveness of heatmaps in driving data-driven decision-making and fostering continuous improvement across diverse industry sectors.
These additional examples demonstrate the versatility of heatmaps in various contexts beyond websites. Whether you're designing software, mobile apps, or optimizing marketing efforts, heatmaps are a valuable asset for data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
Heatmaps Best Practices
To make the most of heatmaps and ensure that you're gathering and interpreting data effectively, it's essential to follow these best practices:
- Set Clear Objectives: Define your goals and objectives for using heatmaps. Whether it's improving user experience, increasing conversions, or optimizing content, having clear intentions guides your heatmap analysis.
- Segment Your Data: Utilize segmentation to analyze specific user groups or behaviors. This provides more granular insights and helps you tailor your strategies accordingly.
- Combine Heatmaps with Other Data: To gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior, integrate heatmap data with other analytics tools and user feedback. This synergy provides a more complete picture.
- Regularly Review Heatmaps: Don't treat heatmap analysis as a one-time task. Regularly review heatmaps to identify trends and patterns over time, ensuring your website remains optimized.
- A/B Testing: Pair heatmap analysis with A/B testing to validate proposed changes and improvements. This approach helps you make data-backed decisions.
- Privacy and GDPR Compliance: Be mindful of user privacy. Inform visitors about data collection through heatmaps and provide options for opting out, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR.
- Responsive Design Testing: Use heatmaps to evaluate how users interact with your website on various devices and screen sizes. Ensure that your design is responsive and user-friendly across platforms.
- Page Load Speed: Monitor page load times and their impact on user behavior. Slow-loading pages can lead to increased bounce rates, affecting heatmap data.
- User Surveys and Feedback: Combine heatmap insights with direct user surveys and feedback. This qualitative data can provide context and deeper understanding.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Share heatmap findings and insights with different teams within your organization, including marketing, design, and development, to implement improvements effectively.
- Iterate and Test: Use heatmap data to drive iterative improvements. Implement changes based on your findings, test their impact, and refine as needed.
- Training and Education: Ensure your team is trained in heatmap analysis and interpretation. A well-informed team can make better use of heatmap data.
By adhering to these best practices, you'll be better equipped to harness the full potential of heatmaps and leverage them as a valuable tool for improving your website, user experience, and overall online success.
Conclusion for Heatmaps
Heatmaps are your trusty companions on the journey to understanding user behavior and improving digital experiences. Whether you run a website, develop products, or engage in marketing campaigns, these visual tools offer crystal-clear insights that can supercharge your efforts.
With heatmaps by your side, you can pinpoint what works, what needs tweaking, and what truly captivates your audience. So, don't hesitate to embrace the heatmap revolution and make data-driven decisions that lead to enhanced user satisfaction, higher conversions, and overall success in the digital realm.
How to Create a Heatmap in Seconds?
In the dynamic world of business, timely decisions are often the key to success. Appinio, a real-time market research platform, empowers you to harness the power of heatmaps and gain invaluable consumer insights in minutes.
Here's why Appinio stands out:
- Speedy Insights: Appinio ensures you're not left waiting. From posing questions to unveiling insights, it's a matter of minutes, not hours or days.
- User-Friendly: No need for a research PhD. Appinio's intuitive platform is designed for anyone to navigate effortlessly, making market research accessible to all.
- Global Reach: Define your target audience with precision from over 1200 characteristics and conduct surveys in more than 90 countries.
Get facts and figures 🧠
Want to see more data insights? Our free reports are just the right thing for you!