What is a Usability Test and How to Conduct It?
Appinio Research · 24.11.2023 · 40min read

Content
Ever wondered how to create a product that users genuinely love and find effortless to use? Usability testing holds the key. It's not just about designing a product; it's about developing one that works seamlessly for the people who use it.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the ins and outs of usability testing, from defining clear objectives to selecting the right tools and software. You'll discover best practices, common pitfalls to avoid, and the iterative process that ensures your product continually evolves to meet user needs. Let's dive into the world of usability testing and unlock the secrets to creating exceptional user experiences.
What is Usability Testing?
Usability testing is a methodical and structured approach to evaluating the user-friendliness and effectiveness of a product or website. It involves real users interacting with the product while performing specific tasks, providing valuable insights into how well the design meets their needs and expectations.
The importance of usability testing lies in its ability to identify usability issues, improve the user experience, and ultimately enhance the product's success in the market. By simulating real-world usage scenarios and gathering user feedback, usability testing ensures that design decisions are based on user insights rather than assumptions.
What is the Purpose of a Usability Test?
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: Usability testing helps uncover and address issues that may frustrate or confuse users. Improving the user experience leads to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduced Development Costs: Identifying and rectifying usability issues early in the design process is more cost-effective than addressing them after a product's launch.
- Competitive Advantage: A user-friendly product stands out in the market, attracting and retaining more users. Usability testing helps you gain a competitive edge.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Usability testing provides tangible data and insights that guide informed design decisions, reducing the risk of product failures.
- Improved Accessibility: Ensuring usability for all users, including those with disabilities, is crucial for compliance and inclusivity.
Benefits of Usability Testing
Usability testing offers a multitude of benefits that contribute to the overall success of a product or website. Here are some key advantages:
- Uncover Usability Issues: Usability testing reveals issues that may go unnoticed during the design phase. It identifies areas of confusion, navigation challenges, and user frustrations, allowing you to address them proactively.
- Enhance User Experience: By making improvements based on usability test results, you create a more intuitive and enjoyable user experience. Users are more likely to engage with and recommend a product that is easy to use.
- Reduce Development Risks: Usability testing reduces the risk of costly design errors. By catching usability issues early, you avoid rework and save resources, leading to a smoother development process.
- Optimize Conversion Rates: For websites and apps, usability testing can directly impact conversion rates. Improved usability often leads to higher conversion rates, whether it's signing up, making a purchase, or completing a desired action.
- Gain Competitive Edge: A product or website that prioritizes usability gains a competitive advantage. Users are more likely to choose and remain loyal to a user-friendly option in a crowded market.
- Align with User Expectations: Usability testing ensures that your product aligns with user expectations and needs. This alignment fosters trust and builds positive user relationships.
- Support Accessibility: Usability testing helps identify and rectify accessibility issues, ensuring that your product is usable by individuals with disabilities, thereby expanding your user base.
Usability testing is a vital step in the design and development process, offering numerous benefits that result in improved user satisfaction, reduced costs, and a competitive advantage in the market. It is a powerful tool for creating products and websites that effectively meet user needs and expectations.
How to Prepare for Usability Testing?
Before you dive into conducting usability tests, it's essential to lay a solid foundation through thorough preparation.
1. Define Clear Objectives and Goals
The first step in preparing for usability testing is to define your objectives and goals. What do you want to achieve with this usability test? Your objectives should be specific, measurable, and aligned with your overall product or website goals. Here's a breakdown of this crucial step:
Why Objectives Matter
Clear objectives serve as the compass for your usability testing process. They help you focus on what truly matters, ensuring that you gather relevant insights to enhance your product's user experience. Objectives provide a framework for:
- Identifying the key areas of your product that need evaluation.
- Setting specific success criteria for the test.
- Guiding the creation of test scenarios and tasks.
Tips for Defining Objectives
- Be Specific: Instead of a vague objective like "Improve user experience," aim for something more precise, such as "Reduce the checkout abandonment rate by 15%."
- Consider User Needs: Your objectives should reflect the needs and pain points of your target users. What issues do they commonly face when using your product?
- Align with Business Goals: Ensure that your objectives align with your organization's broader business and product goals. Usability improvements should contribute to achieving these goals.
- Prioritize Objectives: If you have multiple objectives, prioritize them based on their importance and impact on the user experience.
2. Identify and Understand Your Target Users
To conduct effective usability testing, you need to have a clear understanding of your target users. These are the individuals who represent your product's intended audience. Identifying and empathizing with your users is crucial for creating scenarios and tasks that resonate with their needs and expectations.
User Personas
User personas are fictional representations of your ideal users. Creating user personas can help you and your team gain insights into your users' behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
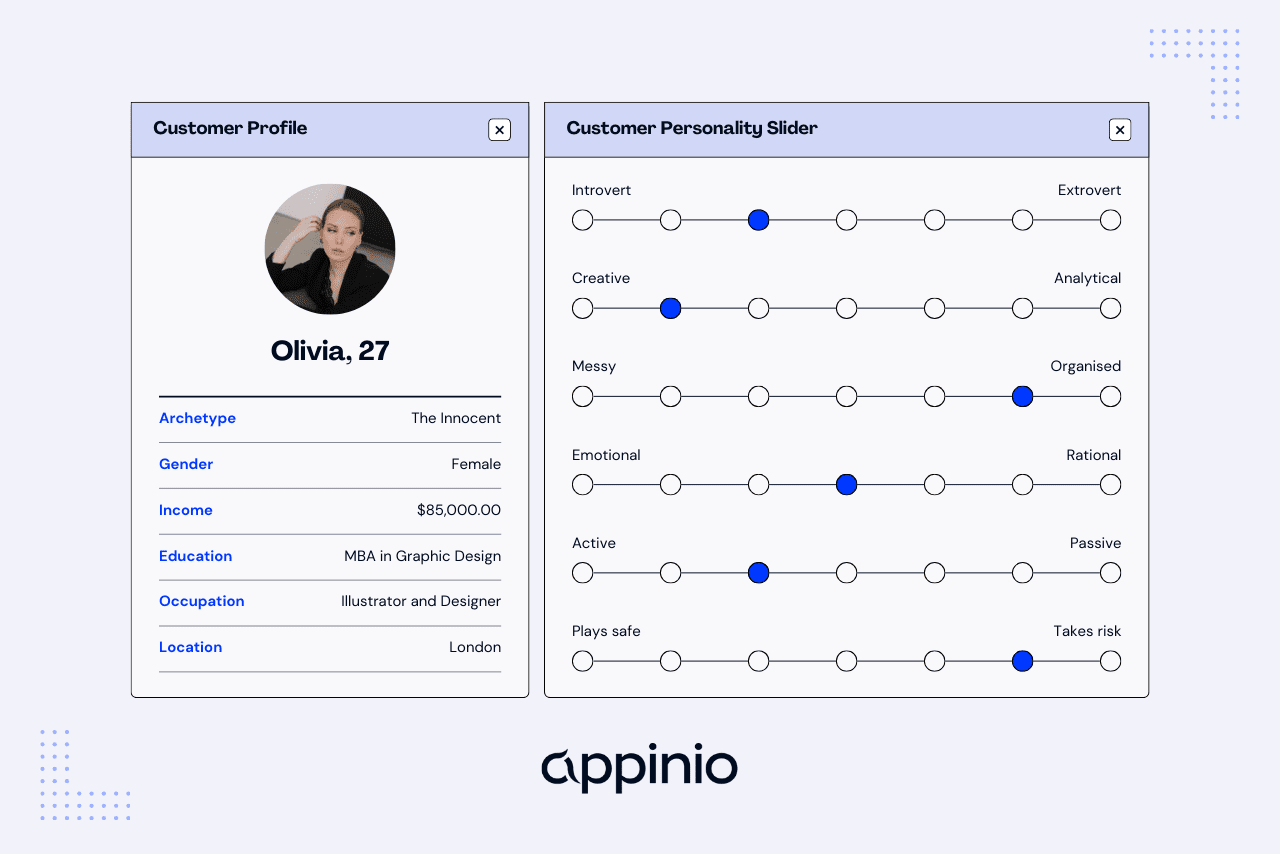
Here's how to develop and utilize user personas effectively:
- Create Detailed Personas: Develop personas that include demographic information, goals, challenges, and preferences. Give your personas names and faces to make them more relatable.
- Use Personas to Inform Testing: When designing usability test scenarios, consider how each persona would interact with your product. Tailor tasks to match the personas' characteristics.
- Empathize with Users: Encourage your team to think from the perspective of these personas to better understand user needs.
3. Choose the Right Usability Testing Methods
Usability testing can take various forms, and choosing the proper method is crucial for obtaining meaningful insights. The choice often depends on factors like your objectives, budget, timeline, and the nature of your product.
Common Usability Testing Methods
- Moderated Usability Testing: In this method, a moderator guides participants through the test while observing their interactions and collecting feedback. It allows for real-time insights and clarifications.
- Unmoderated Usability Testing: Participants complete the test scenarios independently without a moderator present. This method is cost-effective and suitable for remote testing.
- Remote Usability Testing: Participants engage with your product from their own location, often using screen recording and video conferencing tools. It's convenient for both researchers and participants.
- In-Person Usability Testing: Conducted in a controlled environment, this method enables close observation of participants and their interactions with your product.
- Benchmark Testing: Compare the usability of your product against competitors or industry standards to gain insights into where you stand in terms of user experience.
Choosing the Right Method
Consider the following factors when selecting a usability testing method:
- Budget: Determine the resources available for testing, including technology, participant incentives, and personnel.
- Timeline: Assess how quickly you need results. Some methods, like remote testing, can provide faster turnaround times.
- Complexity of Tasks: The nature of your tasks and scenarios may influence the choice of method. For complex interactions, moderated testing may be more suitable.
- Access to Participants: Consider how easily you can recruit and engage with your target users. Remote testing may be more convenient if your users are geographically dispersed.
4. Thoughtful Participant Recruitment
Recruiting the right participants is a critical aspect of usability testing. Your participants should closely match your target audience, ensuring that the feedback you receive is relevant and representative.
Recruitment Strategies
Here are some effective strategies for recruiting usability testing participants:
- Use Online Recruiting Platforms: Websites and platforms dedicated to user testing recruitment can help you find participants who match your criteria.
- Tap Into Existing User Base: If you already have a user base, consider reaching out to them. Existing users can provide valuable insights as they are already familiar with your product.
- Social Media and Forums: Engage with communities related to your product or industry on social media platforms or forums. Seek out participants who are genuinely interested in your product.
- Offer Incentives: To motivate participants, consider providing incentives such as gift cards, discounts, or product samples.
- Screen Participants: Create a screening process to ensure that recruited participants meet your criteria. Screen for characteristics like age, gender, experience level, and familiarity with similar products.
By putting thought and effort into participant recruitment, you'll have a diverse and representative group that can provide valuable feedback during your usability tests. With these preparations complete, you are well on your way to conducting successful usability tests.
How to Create Usability Test Scenarios?
Once you've laid the groundwork by defining objectives, identifying target users, selecting usability testing methods, and recruiting participants, it's time to focus on creating effective usability test scenarios. These scenarios are the heart of your usability testing process, shaping how participants interact with your product and helping you gather valuable insights.
1. Design Realistic Tasks
Designing realistic tasks is a crucial aspect of usability testing. The tasks you create should mirror the real-world actions that users would typically perform when interacting with your product. Here's how to design tasks that resonate with your participants:
Understand User Goals
To create realistic tasks, you must first understand the goals and objectives of your target users. Consider what actions they would take to achieve these goals while using your product. For example, if you're testing an e-commerce website, tasks might include:
- "Find a product you want to purchase and add it to your cart."
- "Navigate to the checkout page and complete the purchase."
Keep Tasks Focused
Avoid overwhelming participants with complex tasks that involve multiple steps. Instead, break down larger tasks into smaller, more manageable subtasks. This approach allows you to pinpoint specific areas where users may encounter difficulties.
Provide Context
When presenting tasks to participants, give them context about their role and the scenario. For example, you might say, "Imagine you are planning a vacation and need to book a flight on this website." Context helps participants immerse themselves in the scenario and approach tasks more realistically.
2. Write Test Scripts
Test scripts are essential documents guiding both the moderator and the participants through the usability test. Well-written test scripts ensure consistency across multiple test sessions and help moderators facilitate the test effectively.
Components of a Test Script
A comprehensive test script should include the following components:
- Introduction: Begin with a brief introduction, welcoming the participant and explaining the purpose of the test.
- Scenario: Present the scenario or context in which the participant will be operating. This sets the stage for the tasks to follow.
- Tasks: List the tasks the participant needs to complete. Each task should be clearly defined, with specific instructions on what actions to take.
- Success Criteria: Specify the criteria for success, explaining what constitutes a successful completion of each task.
- Questions and Probes: Include questions or prompts that the moderator can use to gather additional insights from participants. For example, you might ask, "What were you thinking while trying to complete this task?"
Test Script Language
When writing test scripts, use clear and concise language. Avoid jargon or technical terms that participants may not understand. Make sure that the language aligns with the typical language used by your target users.
3. Create Prototypes or Mockups
Depending on the stage of your product's development, you may need to create prototypes or mockups for usability testing. These visual representations of your product allow participants to interact with it as if it were a fully functional version.

Types of Prototypes
There are various types of prototypes you can use for usability testing:
- Low-Fidelity Wireframes: Simple, grayscale representations focusing on layout and structure without detailed visuals.
- High-Fidelity Prototypes: More thorough and interactive representations that closely resemble the final product. They may include clickable elements and simulate user interactions.
- Paper Prototypes: Hand-drawn or printed representations that can be used in in-person usability tests, where participants interact with paper-based interfaces.
Benefits of Prototyping
Prototypes offer several advantages during usability testing:
- Early Testing: You can conduct usability tests before investing significant development resources in a fully functional product.
- Iterative Design: Prototypes allow for rapid iteration and refinement of your design based on user feedback.
- Realistic Interactions: High-fidelity prototypes provide a more natural user experience, helping you identify usability issues more accurately.
- Cost Savings: Identifying and addressing usability issues at the prototype stage is more cost-effective than making changes after a product is built.
By creating realistic prototypes or mockups and incorporating them into your usability testing process, you can gain valuable insights into how users interact with your product and make informed design decisions.
With usability test scenarios in place and prototypes ready, you're now prepared to move on to the actual usability testing process.
How to Conduct a Usability Test?
Now that you've prepared thoroughly by defining objectives, understanding your target users, creating usability test scenarios, and developing prototypes, it's time to dive into the core of usability testing.
1. Set Up the Testing Environment
Creating the proper testing environment is crucial for obtaining accurate and actionable insights from your usability tests. Whether you're conducting in-person or remote tests, the environment should be conducive to the test's objectives.
In-Person Testing Environment
If you're conducting usability tests in a physical location, consider the following factors:
- Location: Choose a quiet, distraction-free space where participants can focus on the tasks without interruptions.
- Equipment: Ensure that all necessary equipment, such as computers, recording devices, and cameras, is set up and functioning correctly.
- Moderator Setup: Position the moderator's station where they can observe the participant's interactions with the product and take notes without distracting the participant.
- Comfort: Create a comfortable and welcoming environment for participants to put them at ease.
Remote Testing Environment
For remote usability testing, you'll need to consider different aspects:
- Technology: Verify that participants can access the necessary technology and tools, such as screen recording software or remote testing platforms.
- Instructions: Provide clear instructions to participants for setting up their testing environment, including any specific software or settings required.
- Support: Have a plan in place to provide remote technical support to participants if they encounter issues during the test.
Regardless of the testing environment, ensure that it closely replicates how users would typically engage with your product.
2. Moderate the Usability Test
Moderating a usability test involves guiding participants through the test scenarios while observing their interactions and collecting valuable feedback. The role of the moderator is crucial in ensuring the smooth execution of the test.
Moderator Responsibilities
Key responsibilities of the moderator include:
- Explaining the Process: Begin by explaining the purpose of the test, the scenarios, and what is expected of the participant.
- Encouraging Thinking Aloud: Encourage participants to "think aloud" by verbalizing their thoughts and reactions as they navigate the product. This provides insights into their decision-making process.
- Providing Clarity: If participants become confused or stuck during a task, the moderator can give clarifications to keep the test on track.
- Asking Follow-Up Questions: Use predefined questions and probes from the test script to gather additional insights. For example, ask participants why they made specific choices or how they felt during particular interactions.
- Taking Notes: Keep detailed notes on participant behavior, comments, and any usability issues observed during the test.
Moderator Neutrality
Moderators should remain neutral and avoid influencing participants' actions or opinions. It's essential to let participants explore the product independently and form their own conclusions.
3. Collect Data and Observations
During usability testing, you'll gather a wealth of data and observations that will inform your design decisions. It's crucial to capture this information effectively for analysis and reporting.
Data Collection Methods
There are several methods for collecting data during usability tests:
- Video Recording: Record the participant's interactions, including their screen, facial expressions, and verbal comments. Video recordings provide a comprehensive view of the test.
- Note-Taking: Moderators should take detailed notes during the test, documenting participant actions, comments, and any usability issues encountered.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Administer post-test surveys or questionnaires to gather quantitative feedback and ratings from participants.
- Eye Tracking: In some cases, you may use eye-tracking technology to understand where participants are focusing their attention on the interface.
Data Organization
Organize collected data in a structured manner for easier analysis. You can use tools like spreadsheets, data analysis software, or dedicated usability testing platforms to manage and categorize data.
4. Handle Unexpected Issues
Usability tests may encounter unexpected issues or challenges. Being prepared to address these issues promptly is essential to ensure the test's success.
Common Unexpected Issues
Some common issues you may encounter during usability tests include:
- Technical Problems: Participants may experience technical difficulties with the product or their equipment.
- Participant Frustration: Participants might become frustrated or stressed if they encounter usability issues.
- Misinterpretation of Tasks: Participants may misunderstand or misinterpret test tasks, leading to inaccurate results.
Handling Unexpected Issues
To address unexpected issues effectively:
- Stay Calm: As a moderator, remain calm and composed to reassure participants.
- Provide Assistance: Offer assistance when necessary but avoid leading participants to specific solutions.
- Document Issues: Document any unexpected issues or incidents, as they may provide valuable insights for later analysis.
- Adapt as Needed: Be flexible in adapting the test plan if unforeseen issues require changes to the scenarios or tasks.
By addressing unexpected issues with professionalism and adaptability, you can maintain the integrity of the usability test and still gather valuable insights.
With the usability test successfully conducted, you'll move on to the next steps of analyzing the gathered data and reporting your findings. This phase is essential for making informed design improvements based on user feedback.
How to Analyze Usability Test Results?
After conducting usability tests and collecting valuable data, the next crucial step is to analyze the results effectively.
1. Review User Feedback
User feedback is at the core of usability testing. It provides insights into user experiences, pain points, and preferences. To analyze usability test results, you must first review the feedback gathered from participants.
Data Sources
User feedback can come from various sources:
- Observations: Insights gained by observing participants as they interacted with the product.
- Verbal Comments: Comments made by participants during the test, including their thoughts and reactions.
- Survey Responses: Quantitative data collected through post-test surveys or questionnaires.
- Recorded Sessions: Video recordings of the usability test sessions, capturing user actions and expressions.
Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is a popular method for reviewing and organizing user feedback. It involves identifying recurring themes, patterns, or issues in the data. Key steps include:
- Transcribing Data: If not already done, transcribe verbal comments and observations from test sessions.
- Coding Data: Assign codes or labels to segments of data based on common themes or issues. For example, you might code comments related to difficulty with navigation under a "Navigation" category.
- Identifying Patterns: Look for patterns and trends within the coded data. Are there recurring issues or pain points mentioned by multiple participants?
- Summarizing Findings: Summarize the key findings and insights gleaned from the analysis.
2. Identify Usability Issues
Usability issues are aspects of your product that hinder user satisfaction or task completion. Identifying these issues is a critical step in improving the user experience.
Types of Usability Issues
Common usability issues include:
- Navigation Problems: Difficulty in finding information or moving through the product.
- Confusing Terminology: Users may be puzzled by the wording used in the interface.
- Error Messages: Unclear or unhelpful error messages can frustrate users.
- Slow Load Times: Long loading times can lead to user frustration and abandonment.
- Ineffective Calls to Action: Users may not understand what action to take next.
Usability Issue Severity
When identifying usability issues, it's essential to assess their severity. Not all issues are equally critical, and prioritizing them helps in the subsequent steps of improving the product. Severity levels may include:
- Critical: Issues that prevent users from completing essential tasks or that lead to data loss or security risks.
- High: Significant issues that impede user flow or create frustration but don't halt task completion entirely.
- Medium: Issues that are noticeable but don't severely impact usability.
- Low: Minor issues that may cause slight inconvenience but don't significantly affect usability.
3. Prioritize and Categorize Problems
With a list of identified usability issues, the next step is to prioritize and categorize them. This ensures that you address the most critical problems first and allocate resources effectively.
Prioritization Methods
Consider the following factors when prioritizing usability issues:
- Impact on Users: Focus on issues that have the most significant negative impact on user experience.
- Frequency: If multiple participants encounter the same problem, it's likely more critical than a one-off issue.
- Ease of Fix: Some issues may be straightforward to address, while others may require more complex solutions.
- Business Impact: Assess how each issue aligns with your business goals and priorities.
Issue Categories
Categorizing usability issues can help in organizing and addressing them systematically. Common categories include:
- Navigation and Information Architecture: Issues related to how users find and access information within the product.
- Design and Layout: Problems with the visual design, layout, or organization of elements.
- Content and Messaging: Issues related to the clarity and effectiveness of content and messaging.
- Functionality and Interactivity: Problems with the functionality and interactive elements of the product.
By categorizing and prioritizing usability issues, you can create a clear roadmap for addressing them in your product's design and development.
How to Report Usability Testing Findings?
Once you've analyzed usability test results and identified key issues, the next step is to report your findings effectively to stakeholders and provide actionable recommendations. Clear communication is essential to drive improvements in the user experience.
1. Create Usability Test Reports
Usability test reports serve as a comprehensive document summarizing the entire testing process, findings, and recommendations. The report should be well-structured and include the following elements:
Executive Summary
- Brief overview of the usability testing process.
- Key findings and their impact on the user experience.
- High-level recommendations.
Methodology
- Detailed description of the usability testing methods used.
- Information on participant demographics and recruitment.
- Overview of the scenarios and tasks.
Findings
- A breakdown of identified usability issues, categorized by severity.
- Supporting evidence such as quotes, observations, and data.
Recommendations
- Actionable recommendations for addressing each usability issue.
- Prioritization of recommendations based on severity and impact.
Appendices
- Supplementary materials such as test scripts, questionnaires, or raw data.
2. Present Results to Stakeholders
Presenting usability test findings to stakeholders is a critical step in the usability improvement process. It's essential to convey the importance of addressing identified issues and gaining buy-in for necessary changes.
Tailor Communication
Adapt your presentation to your audience. Stakeholders may include designers, developers, product managers, and executives, each with different levels of technical expertise and priorities. Tailor your communication to resonate with their interests and concerns.
Visual Aids
Use visual aids such as charts, graphs, and screenshots to illustrate usability issues and their impact. Graphical representation can make the findings more accessible and memorable.
Interactive Demonstrations
Whenever possible, demonstrate usability issues and improvements through interactive prototypes or live testing. Seeing issues in action can be more convincing than descriptions alone.
3. Providing Recommendations
Recommendations are a crucial component of your usability test report. They guide the actions that need to be taken to improve the user experience.
- Be specific and actionable: Clearly state what changes or improvements should be made.
- Be focused: Prioritize recommendations based on severity and impact.
- Include evidence: Support your recommendations with data, observations, and user feedback.
- Collaborate: Involve relevant stakeholders in discussions about implementing recommendations.
By providing clear, actionable recommendations, you help ensure that usability issues are addressed effectively, leading to a better user experience for your product or website.
With usability test results analyzed, reported, and communicated effectively, you've taken significant steps toward improving your product's user experience. The next phase involves implementing changes based on the recommendations and continually monitoring progress through iterative usability testing.
Iterative Usability Testing
Usability testing is not a one-time effort but a continuous process aimed at enhancing the user experience over time. Iterative usability testing involves implementing changes and improvements based on earlier test results, repeating usability testing as needed, and continuously monitoring progress.
1. Implement Changes and Improvements
After analyzing usability test results and identifying usability issues, it's time to take action by implementing changes and improvements to your product or website. This step is crucial for addressing the identified problems and enhancing the overall user experience.
Prioritize Recommendations
Begin by prioritizing the recommendations from your usability test report. Focus on addressing critical and high-severity issues that have the most significant impact on user satisfaction and task completion.
Design and Development
Work closely with your design and development teams to implement the recommended changes. Depending on the nature of the issues, this may involve redesigning user interfaces, adjusting functionality, revising content, or optimizing performance.
Usability Testing of Changes
Before implementing changes in a production environment, consider conducting additional usability testing on the updated design or features. This testing can help verify that the changes have indeed improved the user experience as intended.
2. Repeat Usability Testing
Iterative usability testing involves periodically revisiting the testing process to ensure that your product continues to meet user needs and expectations. It's not uncommon to conduct multiple rounds of usability testing throughout the product's lifecycle.
Timing of Repeated Testing
The timing of repeated usability testing can vary depending on factors such as the frequency of product updates, the scope of changes, and user feedback. Consider the following scenarios for repeating usability testing:
- After implementing significant design or feature changes.
- When introducing new features or functionalities.
- In response to evolving user needs or industry standards.
- On a regular schedule (e.g., quarterly or annually) to proactively assess and improve the user experience.
Test Focus
When repeating usability testing, you can choose to focus on specific areas or features of your product that have been modified or updated. This targeted approach allows you to assess the impact of changes more effectively.
Compare Against Baseline
Use the results from your initial usability tests as a baseline for comparison. This helps you measure the effectiveness of the changes made since the last round of testing.
3. Monitor Progress
Monitoring progress is an ongoing aspect of iterative usability testing. It involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), gathering user feedback, and continuously assessing the user experience to ensure that improvements are sustained.
Usability Testing KPIs
Define and track KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that align with your usability objectives. Common KPIs include:
- Task Completion Rate: The percentage of users who successfully complete key tasks without errors or issues.
- User Satisfaction: Gather user feedback through surveys or ratings to gauge overall satisfaction.
- Conversion Rates: Measure the impact of usability improvements on conversion rates, such as sign-ups or purchases.
- Time on Task: Assess whether users can complete tasks more efficiently after improvements.
User Feedback Mechanisms
Continue collecting user feedback through various channels, including customer support, surveys, and direct user interactions. User feedback provides valuable insights into ongoing usability issues and user preferences.
Usability Testing at Scale
Consider scaling your usability testing efforts as your product grows. This may involve larger sample sizes, remote testing with geographically diverse users, or automated usability testing tools.
Continuous Improvement
Usability testing should be seen as an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Regularly review and refine your usability testing methodology based on lessons learned and changing user needs.
By implementing changes, repeating usability testing, and monitoring progress iteratively, you can ensure that your product or website maintains a high level of usability and user satisfaction over time.
Usability Testing Best Practices
Usability testing is a valuable process for improving the user experience of your product or website. To ensure the effectiveness of your usability testing efforts, follow these best practices:
- Clear Objectives: Start with well-defined objectives that outline what you want to achieve with usability testing. Clear objectives provide direction and focus for the entire process.
- User-Centered Design: Emphasize user-centered design principles throughout your product's development, with usability testing as a recurring component of your design process.
- Realistic Scenarios: Design real test scenarios and tasks that align with how users would naturally interact with your product in their day-to-day activities.
- Diverse Participant Selection: Recruit a diverse group of participants that reflects your target user base. Include users with varying levels of experience and backgrounds.
- Moderator Neutrality: Moderators should remain neutral and avoid influencing participants' actions or opinions during testing.
- Think-Aloud Protocol: Encourage participants to verbalize their thought processes while completing tasks. This provides insights into their decision-making.
- Usability Metrics: Use usability metrics such as task completion rates, time on task, and error rates to quantify and compare the effectiveness of design improvements.
- Continuous Iteration: Embrace an iterative approach to usability testing. Regularly revisit and improve your product based on test results and user feedback.
- Accessibility Testing: Ensure that usability testing includes participants with disabilities to identify and address accessibility issues.
- Usability Testing Tools: Utilize appropriate usability testing tools and software to streamline the testing process, gather data effectively, and support analysis.
- Feedback Integration: Integrate user feedback from various sources, including usability testing, customer support, and user surveys, to drive continuous improvement.
- Usability Testing Culture: Foster a culture of usability testing within your organization, where all team members understand its value and are involved in the process.
Usability Testing Challenges
Usability testing, while valuable, can encounter pitfalls that hinder its effectiveness. To ensure successful usability testing, be aware of and avoid these common pitfalls:
- Biased Moderation: Moderators should remain impartial and avoid leading participants or providing too much guidance, as this can influence results.
- Small Sample Sizes: Testing with a small number of participants may not uncover all usability issues. Aim for a representative sample size to improve reliability.
- Overcomplicated Tasks: Complex or ambiguous tasks can frustrate participants and skew results. Keep tasks clear and straightforward.
- Failure to Define Objectives: Conducting usability testing without clear objectives can result in a lack of focus and meaningful insights. Define objectives from the outset.
- Ignoring Negative Feedback: Dismissing or ignoring negative feedback from usability testing can lead to missed opportunities for improvement. Take all feedback seriously.
- Inadequate Preparation: Rushing into usability testing without thorough preparation can result in logistical challenges, poor participant recruitment, and wasted resources.
- Not Testing Early Enough: Waiting until late in the development process to conduct usability testing can limit your ability to make significant design changes.
- Limited Accessibility Testing: Neglecting to test for accessibility can exclude users with disabilities and result in compliance issues.
- Neglecting Post-Test Analysis: Completing usability testing without comprehensive post-test analysis can lead to valuable data going unused. Analyze results thoroughly.
- Lack of User Empathy: Failing to empathize with users' perspectives and struggles can lead to overlooking critical usability issues.
- Overlooking Mobile and Responsive Design: Neglecting to test usability on mobile devices or responsive design can miss issues affecting a significant portion of users.
- Ignoring Cultural Differences: Usability can vary across cultures and regions. Consider cultural factors when conducting global usability testing.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you can enhance the effectiveness of your usability testing efforts and ensure that the user experience of your product or website continues to improve over time.
Conclusion for Usability Testing
Usability testing is a powerful tool for enhancing the user experience of your product or website. By following best practices, you can gain valuable insights into how users interact with your design, uncover usability issues, and make informed improvements. Remember to define clear objectives, recruit diverse participants, and maintain a user-centered approach throughout your design process. Usability testing is not a one-time task but a continuous journey of improvement. By avoiding common pitfalls and embracing an iterative approach, you can create a product that truly meets the needs and expectations of your users.
Additionally, selecting the right usability testing tools and software can streamline the process, making it more efficient and effective. These tools, along with user feedback and post-test analysis, play a crucial role in driving positive changes in your design. Usability testing is a collaborative effort that involves your entire team, fostering a culture of user-centered design. With each round of testing and every design iteration, you'll move closer to delivering a product that not only meets but exceeds user expectations, resulting in higher user satisfaction and success in the competitive digital landscape.
How to collect survey data for Usability Testing in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio, the real-time market research platform that empowers you to revolutionize your usability testing process. With Appinio, you can collect invaluable consumer insights swiftly, making data-driven decisions effortlessly. Here's why Appinio is your go-to choice:
- Lightning-Fast Results: From posing questions to obtaining insights, it takes mere minutes. Get the answers you need in record time.
- User-Friendly Interface: No need for a research PhD. Our intuitive platform ensures that anyone can navigate and conduct research seamlessly.
- Global Reach: Reach your target audience across 90+ countries with the ability to define the right demographics from over 1200 characteristics.
Get facts and figures 🧠
Want to see more data insights? Our free reports are just the right thing for you!